Introduction
Ancient Indian philosopher Maharishi Kanad and Greek philosophers Democritus and Leucippus proposed that matter could be divided into smaller particles until reaching an indivisible point. Kanad called these smallest particles Parmanu, while Democritus named them atoms. These were philosophical ideas without experimental proof until the eighteenth century. By then, scientists began to understand the differences between elements and compounds. Antoine Lavoisier significantly contributed to chemistry by establishing the laws of conservation of mass and definite proportions, which explained how elements combine to form compounds, laying the foundation for modern chemical science.
Class 9 Science Atoms and Molecules
Laws of Chemical Combination
The rules based on which different elements or compounds combine with each other to form new compounds are called laws of chemical combination.
There are two laws of chemical combination.
1. Law of conservation of mass
This law was given by Lavoisier in 1774. According to the law of conservation of mass, mass is neither created nor destroyed in any chemical reaction, that is, in any chemical reaction the mass of the reactants remains equal to the mass of the products.
TOTAL MASS OF REACTANTS = TOTAL MASS OF PRODUCTS
2. Law of constant proportion
This law was given by Proust in 1779. According to this law, the elements present in every pure chemical compound are found in a fixed weight ratio, no matter by what method it is made or obtained.
“In a chemical substance, the elements are always present in definite proportions mass”
Dalton’s atomic theory
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, every element is made up of many microscopic particles, which are called atoms. An atom is an indivisible particle of an element, which can participate in any chemical reaction.
The various postulates (or assumptions) of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter are as follows:
- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms, which participate in chemical reactions.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound
Drawbacks of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
It is now known that some of the statements of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter are not exactly correct.
Some of the drawbacks of the Dalton’s atomic of matter are given below:
- One of the major drawbacks of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter is that atoms were thought to be indivisible (which cannot be divided). We now know that atoms can be further divided into still smaller particles called electrons protons and neutrons. So, atoms are themselves made up of three particles: electrons, protons and neutrons.
- Dalton’s atomic theory says that all the atoms of an element have exactly the same mass. It is, however, now know that atoms of the same element can have slightly different masses.
- Dalton’s atomic theory says that atoms of different elements have different masses. It is, however, now known that even atoms of different elements can have the same mass.
Atom
The smallest particle of an element, which takes part in a chemical reaction, but cannot remain in an independent state, is called an atom.
- Atoms are very, very small in size.
- The size of an atom is indicated by its radius which is called ‘atomic radius’ (radius of atom).
- Atomic radius is measured in ‘nanometers’ The symbol of a nanometer is nm.
Symbols of Elements
Dolton’s Symbols of Elements
- Dolton’s was the first scientist to use the symbols to represent elements shortly
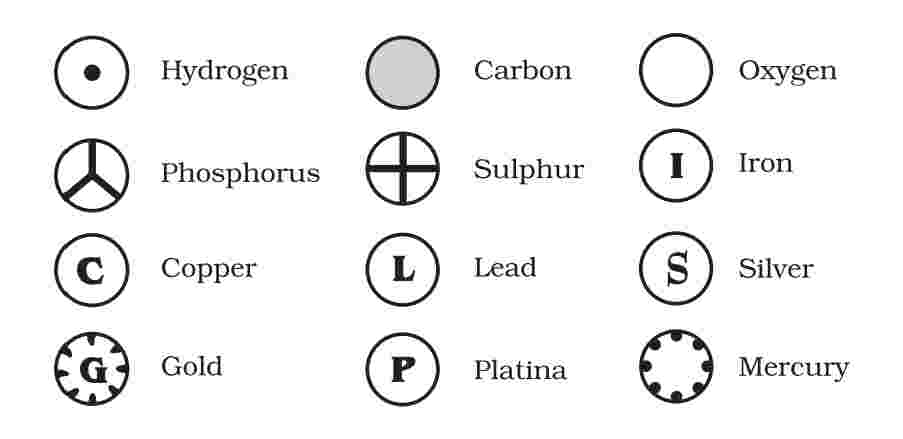
Modern Symbols of Elements
It was J.J. Berzelius who proposed that the first letter (or the first letter and another letter) of the name of an element be used as its symbol. This idea led to the modern symbols of elements.
- Now-a-days, IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is an international scientific organization that approves names of elements, symbols and units.
- Note: The first capital letter of the English name is used to represent symbolic elements. If the names of two elements (of the English alphabet) start with the same letter, then their symbols are made by combining the first two letters of their English names. In that, the first letter is written as a capital letter and the second letter is written as a small letter.
Symbols of some Elements
| Element | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Aluminium | Al |
| Argon | Ar |
| Barium | Ba |
| Boron | B |
| Bromine | Br |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Carbon | C |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Cobalt | Co |
| Copper | Cu |
| Fluorine | F |
| Gold | Au |
| Hydrogen | H |
| Iodine | I |
| Iron | Fe |
| Lead | Pb |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Neon | Ne |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Oxygen | O |
| Potassium | K |
| Silicon | Si |
| Silver | Ag |
| Sodium | Na |
| Sulphur | S |
| Uranium | U |
| Zinc | Zn |
Atomic weight/mass of Elements
The atomic weight of an element is a number that shows how many times an atom of the element is heavier than 1/12th of an atom of C-12.
Atomic masses of a few elements
| Element | Atomic Mass (u) |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 |
| Carbon | 12 |
| Nitrogen | 14 |
| Oxygen | 16 |
| Sodium | 23 |
| Magnesium | 24 |
| Sulphur | 32 |
| Chlorine | 35.5 |
| Calcium | 40 |
Atomic Mass Unit
The mass of 1/12th of an atom of C-12 is called the atomic mass unit. It is represented by amu.
- Average Atomic Weight/mass: The average of the atomic weights of all the isotopes of an element available in nature (in 1%) is called average atomic weight.
Question: How do Atoms Exist?
Answer: A molecule is a group of two or more atoms which are held together strongly by some kind of attractive forces. Such an attractive force holding the atoms together is called a chemical bond
Molecule
The smallest particle of any substance that can exist in an independent state and which contains all the properties of the substance is called a molecule.
There are two types of molecules
- Molecules of elements.
- Molecules of compounds.
Atomicity
The number of atoms present in one molecule of an element is called its atomicity.
- The atomicity of an element is indicated by writing the number as a subscript on the right-hand side bottom of the symbol. For example, H₂ shows that the atomicity of hydrogen is 2. P₁ shows that the atomicity of phosphorus is 4, He shows that the atomicity of helium is 1.
Based on their atomicities, the elements may be classified as monoatomic, triatomic, tetratomic, etc.
| Atomicity | Name of the class | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Monoatomic | i) Noble gases: Helium (He), Argon (Ar), Neon (Ne), Krypton (kr) ii) Metals ( Exist as a large cluster ): Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Aluminium (AI) iii) Carbon (C) |
| 2 | Diatomic | Hydrogen (H₂), Oxygen (O₂), Chlorine (Cl2), Fluorine (F₂), Nitrogen (N₂) |
| 3 | Triatomic | Ozone (O3) |
| 4 | Tetratomic | Phosphorus (P4) |
| More than 4 | Poly atomic | Sulphur (S8), Fullerenes (C60) |
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the masses of all its constituent atoms.
- For ionic compounds, the formula unit mass is the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms (or ions) shown in their formula. •
Calculation of Molecular Mass
As molecules are made up of two or more atoms of the same or different elements, and each atom has a definite atomic mass therefore Molecular mass can be calculated by adding atomic masses of all the atoms present in one molecule of the substance.
Ions
lons are electrically charged species. An ion is formed by the loss or gain of electrons by an atom, so it contains an unequal number of electrons and protons.
There are two types of ions:
Positively Charged lon (Cation)
An anion is formed by the gain of one or more electrons by an atom. An anion contains more electrons than a normal atom. Due to more electrons than protons, an anion has a negative charge on it.
Negatively Charged lon (Anion)
An anion is formed by the gain of one or more electrons by an atom. An anion contains more electrons than a normal atom. Due to more electrons than protons, an anion has a negative charge on it.
Valency
Valency is the combining capacity of an element.
Or
The number of electrons gained, lost, or shared by the atom of an element to achieve stability is called the valency of the element.
Or
Combination of an element/radical (ion) with other elements/radicals Its ability to do is called its connectivity.
- Valency can be used to determine how the atoms of one element will combine with the atoms of another element to form a chemical compound.
Names and symbols of some ion
| Valency | Name of ion | Symbol | Non-metallic element | Symbol | Polyatomic ions | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sodium | Na+ | Hydrogen | H+ | Ammonium | NH4+ |
| Potassium | K+ | Hydride | H− | Hydroxide | OH− | |
| Silver | Ag+ | Chloride | Cl− | Nitrate | NO3− | |
| Copper (I)* | Cu+ | Bromide | Br− | Hydrogen carbonate | HCO3− | |
| 2. | Magnesium | Mg2+ | Oxide | O2− | Carbonate | CO32− |
| Calcium | Ca2+ | Sulphide | S2− | Sulphite | SO32− | |
| Zinc | Zn2+ | Sulphate | SO42− | |||
| Iron (II)* | Fe2+ | |||||
| Copper (II)* | Cu2+ |
Chemical Formulae
The chemical formula of a compound is based on the symbols of the elements present.
Shows the composition of the molecule of the compound in relation.
| Check it 👇 |
|---|
| CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules? MCQ’s (Comming Soon ) |
| CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules? pdf link click here (coming soon) |
| CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules? pdf link click here (coming soon) |
We hope that provided CBSE Class 9 Science Notes, “Atoms and Molecules,” will be helpful to you. If you have any queries regarding the NCERT Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 3, please drop a comment below, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
