| Class | 9th |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Gravitation |
Gravitational Force
Mutual force of attraction between the objects is called gravitational force.
Universal Law of Gravitation
Every object in the universe attract every other object with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
This force acts along the line joining the centres of the two objects.
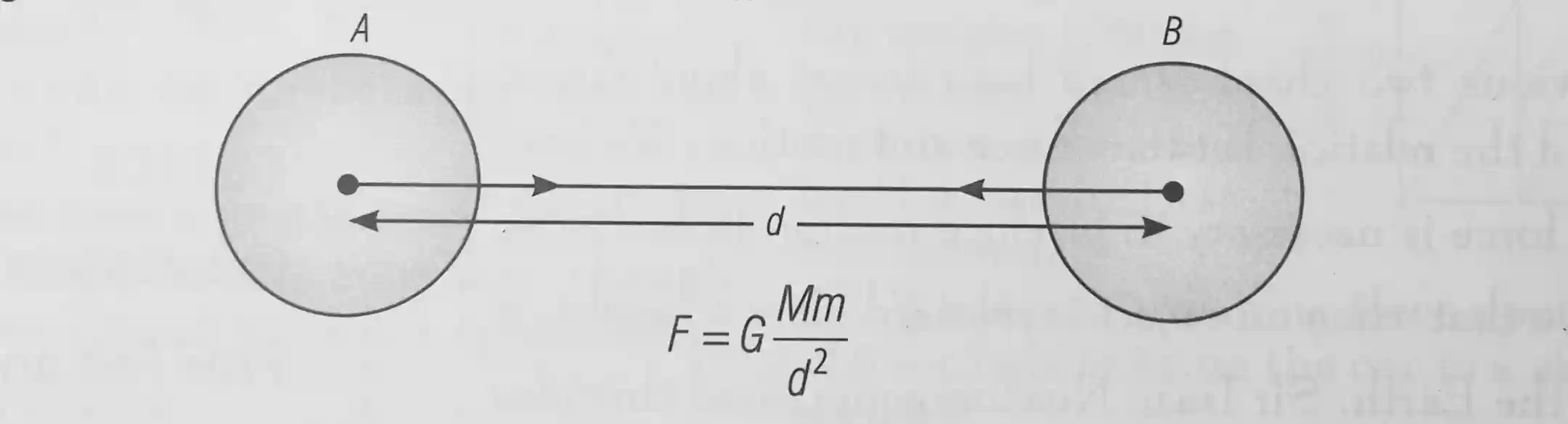
let two object A and B of masses M and m lie at a distance d from each other as shown in the figure above. Let the force of attraction between two objects be F.
According to the universal law of gravitation, the force between the two objects is directly proportion to the product of their masses, ie.,
F∝M×m ...........(i)
And the force between the two objects inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, i.e.,
F∝\frac{1}{d^{2}} ......(ii)
Combining equation (i) and (ii), we get
F∝\frac{M×m}{d^{2}}
F=G\;\frac{M×m}{d^{2}}
Where, G is the constant of proportionality and is called the universal gravitational constant.
G=6.673×10^{−11}\;Nm^{2}/kg^{2}
The value of universal gravitational constant was first determined by experimentally by an english physicist Henry Cavendish by using an extremely sensitive torsion balance in 1798.
Newton’s universal law of gravitation is also known as inverse-square law.
Importance of the universal law of gravitation
1. The gravitational force of attraction of earth is responsible for binding all the terrestrial body on the earth.
2. The gravitational force of the Earth is responsible for the holding the atmosphere around the Earth.
3. Gravitational force of the Earth is also responsible for the rainfall and snow fall on the Earth.
4. The flow of water in rivers is also due to gravitational force of the Earth on water.
5. All the planets revolve around the Sun due to gravitational pull of the Sun on the planets. Thus, gravitational force alone is responsible for holding our solar system.
6. The tides formed by the rising and falling of water level in the ocean are due to the gravitational force of attraction, which the Sun and Moon exert on sea water.
Free Fall
Whenever objects fall towards Earth under the action of gravitational force of Earth alone, we say that the object are in the state of free fall.
Acceleration Due to Gravity
The acceleration produced in a body due to the gravitational pull of the earth near its surface is called acceleration due to gravity.
- It is denoted by small g
- The SI unit of g is m/s²
The gravitational force acting on a body of mass m near the surface of the Earth is given by
F=\frac{M×m}{R^{2}} ….(i)
Where m is the mass of the body, M is the mass of the Earth, and R is the radius of the Earth.
If g is the acceleration produced in a body of mass m, then
F=m×g .....(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii),
mg=G\frac{m×M}{R^{2}}
g=G\frac{M_{e}}{R^{2}_{e}} ....(iii)
Now we know that
Msss of Earth, Me = 6×1024 kg
Radius of earth, Re = 6.4×106 m
Universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67×10-11 Nm²/kg²
Putting the values in the above equation (iii)
g=\frac{6.67×10^{−11}×6×10^{24}}{(6.4×10^{6})^{2}}
g=9.8\;m/s^{2}
The direction of g is along the line joining the body to the body to the centre of Earth.
The value of g does not depend upon the mass of the body.
The relation between g and G
g=\frac{GM}{R^{2}}
Motion of Objects under the Influence of Gravitational Force of the Earth
From general equation of motion, we obtain the following equations of the motion for freely falling bodies:
| General Equations of Motion | Equation of Motion for Freely Falling Bodies |
| (i) v = u + at | (i) v = u + gt |
| (ii) s = ut + 1/2at² | (ii) h = ut + ½gt² |
| (iii) v² = u² + 2as | (iii) v² = u² + 2gh |
The following point must be kept in mind while solving numericals problem on freely falling bodies
- When a body is thrown vertically upward its final velocity v become zero.
- When a body drop from a certain height it’s initial velocity u is taken as zero.
- Acceleration due to gravity G is taken as negative when a body is thrown vertically upward (g= -9.8 m/s²)
- Acceleration due to gravity ji is taken as positive and a body is drop from a certain height (g = +9.8 m/s²)
- Time taken by the body to reach the highest point is equal to the time it takes to fall from the same height.
Mass
Mass is the quantity of matter contained in the body.
- SI unit of mass is kg.
- Mass is a scalar quantity.
- Mass is the measure of its inertia.
Weight
Weight of a body is the force with which the Earth attracts a body.
Weight=mass×acceleration\;due\;to\;gravity
∴W=m×g
- The SI unit of weight is newton.
- It is a vector quantity.
Weight of an object on the moon
Weight\;of\;object\;on\;the\;moon=\frac{1}{6}×its\;weight\;on\;Earth
Fluid Statics
The branch of physics dealing with the properties of fluids at rest is known as fluid statics or hydrostatics.
Thrust
The force acting perpendicular to a surface is called thrust.
- It is a vector quantity.
- It’s SI unit is same as that of force i.e. , newton
Pressure
The perpendicular force acting on a unit area of the surface is called pressure.
Pressure = Thrust/Area
P = F/A
- SI unit of pressure is pascal or N/m².
- Pressure is a scalar quantity.
Note: The effect of force is decreased by increasing the area on which it acts.
Practical applications of thrust:
- The nails have pointed ends so that the surface area of the nails in contact with the wall is very less. As result, for a given force, more pressure acts on it to easily pierce into the wall.
- The shoulder bags have broad handles. With an increase in area of the handles, the pressure exert by the handles on shoulders of the person is reduced.
- The trucks and buses usually have 6 to 8 tyres.More number of tyres increases the surface area in touch with the roads. With an increase in area, the pressure is reduced and the truck and bus can easily move.
Pressure Exerted By Fluids
Substances that have the ability to flow are called fluids. All liquids and gasses are called fluids in science.
Pressure exerted in any confined mass of fluid is transmitted equally in all direction.
Expression for Pressure Exerted by a Liquid at a Point
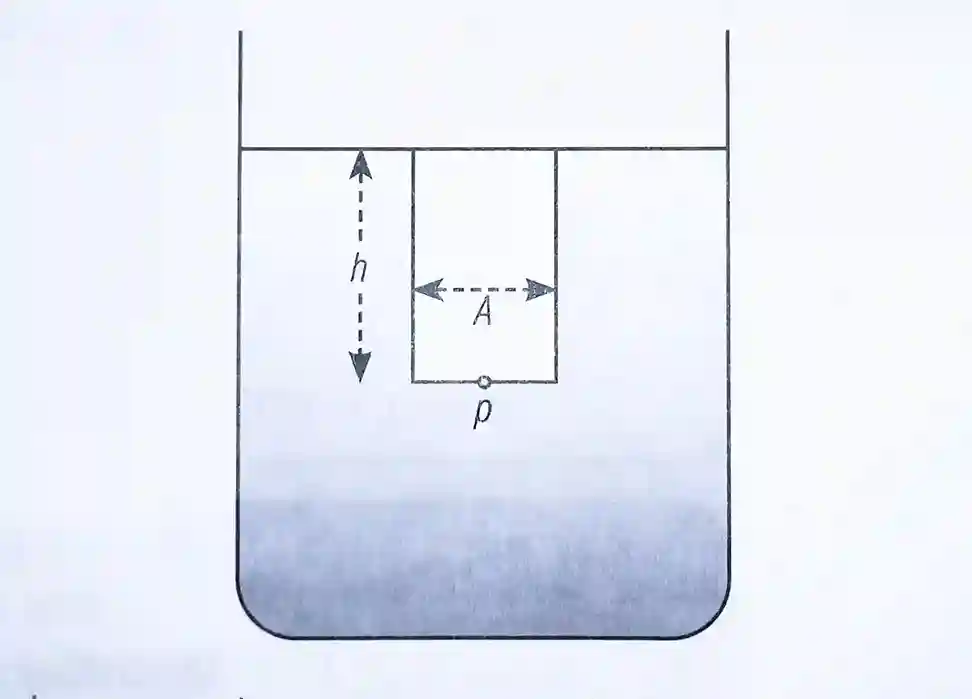
Let us consider a cylindrical column of the liquid of height h, and cross-sectional area A. If d is the density of the liquid,
Mass of the liquid in column = A×h×d
If g is the acceleration due to gravity,
Weight of the liquid in the column= Mass × Acceleration due to gravity
Weight of the liquid in the column= A h d × g
Weight of the liquid in the column= A h d g
Therefore, thrust at the base of the cylindrical column of the liquid = A h d g
Then, pressure exerted by the liquid at the depth of h (at point P)= Thrust/Area
P= A h d g/A
P= h d g
Thus pressure at a point in a liquid is proportional to its depth, density and acceleration due to gravity. This shows that at any place, inside a liquid, all points at the same depth are the same pressure.
Buoyancy or Upthrust
When a body is partially or Holy immersed in a liquid and upward force acts on it which is called up thrust or buoyant force.
The tendency of a fluid exert an upward force on an object placed in it is called buoyancy.
Factors on which buoyancy depends
- Size and volume of the body merged in the fluid
- Density of the fluid in which the body is immersed.
- Acceleration due to gravity at that place.
- Temperature of the fluid.
Buoyant Force (Fb)= V d g
where
V = volume of the object
d = density of the object
g = Acceleration due to gravity
mass m = V d
Floating and sinking of the object in liquid
The simple points to remember for an object when fully immersed in a liquid are:
1. If the upthrust is more than the weight of an object then the object floats, or if the density of an object is less than the liquid, it floats.
2. If the upthrust is less than the weight of an object, then the object sinks, or if the density of an object is more than the liquid, it sinks.
Archimedes’ Principle
When a body is partially or wholly immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upthrust (or apparently loses its weight), which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the immersed part of the body.
Application of Archimedes’ Principle
Archimedes’ principle is applied:
(i) In designing ships and submarines.
(ii) Determining milk purity.
(iii) Determining fluid density.
(iv) Determining volume of an object.
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
Density = Mass /Volume
- SI unit of density is kg/m³.
- It is a scalar quantity.
The density of pure water is 1000 kg/m³.
Floatation
- If the density of the body is more than the density of water, the object will sink in water.
- If the density of the body is equal to the density of water, the object will remain submerged completely at any level in the water.
- If the density of the body is less than the density of water, the object will float on the surface of water.
According to principle of floatation an object will float in a liquid if the weight of the object is equal to the weight of liquid displaced by it
Weight of Object = Weight of liquid displaced by it.
FAQ
-
What is the properties of gravitational force?
(i) Gravitational force is an attractive force.
(ii) Gravitational force is directly proportional to product of masses of the two particles.
(iii) Gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two particles. -
What do you mean by free fall?
When an object falls under gravitation force only without air resistance then the motion of an object is called free fall.
-
What are the difference between the mass of an object and its weight?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the gravitational force exerted by the mass on that object.
-
What is the acceleration of free fall?
9.8 m/s²
-
What do you mean by buoyancy?
The tendency of a fluid to exert upward force on an object placed inside it is called buoyancy.
-
Which force holds the atmosphere around Earth?
Gravitational force.
-
What is the universal law of gravitation?
Every object in the universe exerts a force of attraction on every other object that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
-
What is gravitation?
Gravitation is the force that pulls two masses towards each other.
-
What is gravitational force?
Mutual force of attraction between the objects is called gravitational force.
-
Why G is called universal constant?
The value of g is independent of the nature, size and mass of the interacting bodies, the space where the particles are kept, and the time at which the force is considered, So G is called a universal constant.
