⚡ Class 10 Physics MCQ PYQ 2024–25 with Answers includes important multiple-choice questions asked in the latest board exams. These questions are strictly based on the Class 10 Physics syllabus and follow the current exam pattern. Practicing previous year MCQs helps students understand key concepts, identify important topics, and improve accuracy in exams. This content is useful for quick revision, self-assessment, and effective board exam preparation.
1. Light: Reflection and Refraction
Reflection
1. In order to obtain large images of the teeth of patients, the dentist holds the concave mirror in such a manner that the teeth are positioned
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) at the focus of mirror.
(B) between pole and focus of the mirror.
(C) between focus and centre of curvature of the mirror.
(D) at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
View Answer
✅ Correct Answer: (B) between pole and focus of the mirror.
📝 Explanation :
When an object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, it forms a virtual, erect, and magnified image, which helps the dentist see enlarged teeth clearly.
2. A candle flame is placed in front of the reflecting surface of a convex mirror of focal length f. If the distance of the flame from the pole of the mirror is ‘f’, its image is formed:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) at infinite distance from the mirror
(B) behind the mirror at the principal focus
(C) behind the mirror at a distance 2f
(D) behind the mirror at a distancef/2
View Answer
Answer: (D) behind the mirror at a distance f/2 ✅
📝 Explanation:
For a convex mirror, the focal length is taken as positive.
Given:
Object distance, u = −f
Focal length, f = +f
Using the mirror formula:
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
1/f = 1/v − 1/f
1/v = 2/f
v = f/2
The positive value of v shows that the image is formed behind the mirror.
Hence, the image is formed behind the mirror at a distance f/2.
3. An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of a concave mirror. If its real and inverted image is formed at 60 cm in front of the mirror, the focal length of the mirror is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) -15 cm
(B) -20 cm
(C) + 20 cm
(D) + 15 cm
View Answer
Answer: (B) −20 cm ✅
📝 Explanation:
Given:
Object distance (u) = −30 cm
Image distance (v) = −60 cm
(Image is real and inverted, formed in front of the concave mirror)
Using mirror formula:
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
1/f = 1/(−60) + 1/(−30)
1/f = (−1 − 2)/60
1/f = −3/60
1/f = −1/20
Focal length (f) = −20 cm
4. Identify from the following the ray diagram which shows the correct path of the reflected ray for the ray incident on concave mirror as shown
[CBSE 2024-25]
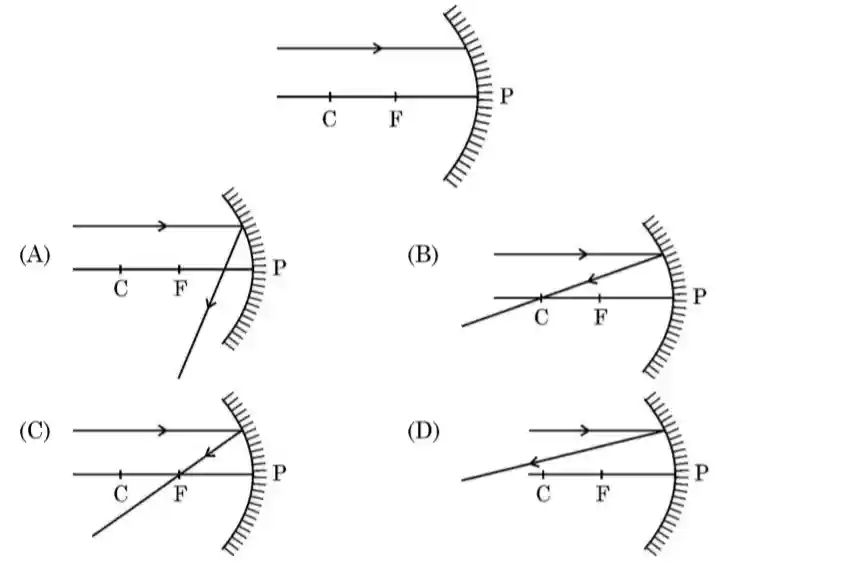
View Answer
Answer: (C) ✅
📝 Explanation: A ray parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror, after reflection, passes through the focus (F)
5. Mirror ‘X’ is used to concentrate sunlight in solar furnace and Mirror ‘Y’ is fitted on the side of the vehicle to see the traffic behind the driver. Which of the following statements are true for the two mirrors?
(i) The image formed by mirror ‘X’ is real, diminished and at its focus.
(ii) The image formed by mirror ‘Y’ is virtual, diminished and erect.
(iii) The image formed by mirror ‘X’ is virtual, diminished and erect.
(iv) The image formed by mirror ‘Y’ is real, diminished and at its focus.
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B)(ii) and (iii)
(C)(iii) and (iv)
(D)(i) and (iv)
View Answer
Answer: (A) (i) and (ii) ✅
📝 Explanation:
Mirror Y (convex mirror) forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image, suitable for rear-view mirrors
Mirror X (concave mirror) forms a real image at the focus when sunlight (parallel rays) is concentrated
6. An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the reflecting surface of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. The image formed is
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Virtual and magnified
(B) Virtual and diminished
(C) Real and magnified
(D) Real and diminished
View Answer
Answer: (C) Real and magnified ✅
📝 Explanation:
Radius of curvature (R) = 40 cm
Focal length of concave mirror,
f = R / 2 = 40 / 2 = 20 cm
Object distance = 30 cm
Since the object is placed between F (20 cm) and C (40 cm),
a concave mirror forms a real, inverted, and magnified image.
Therefore, the image formed is real and magnified.
7. To get an image of magnification -1 on a screen using a lens of focal length 20 cm, the object distance must be:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(a) Less than 20 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 40 cm
(d) 80 cm
View Answer
Answer: (c) 40 cm ✅
📝 Explanation:
Magnification (m) for a lens is given by:
m = v / u
Given magnification, m = −1
Negative sign shows that the image is real and inverted and |m| = 1 means the image is of the same size as the object.
For a convex lens, an image of the same size is formed when the object is placed at 2f.
Given focal length, f = 20 cm
So, object distance = 2f = 2 × 20 = 40 cm
Hence, the object must be placed at a distance of 40 cm.
Refraction
1. If the absolute refractive indices of two media X and Y are 6/5 and 4/3 respectively, then the refractive index of Y with respect to X will be :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) 10/9
(B) 9/10
(C) 9/8
(D) 8/9
View Answer
Answer: (A)10/9 ✅
📝 Explanation: Refractive index of Y with respect to X
2. Consider the following ray diagram:
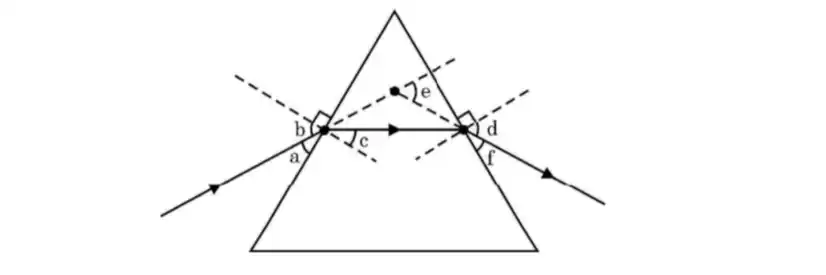
Here the angel of incidence and angel of deviation respectively are
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) a and e
(B) b and d
(C) b and e
(D) a and f
View Answer
Answer: (C) b and e ✅
📝 Explanation:
- Angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray → e
- Angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal at the first surface → b
3. If the absolute refractive indices of two media X and Y are 6/5 and 4/3 respectively, then the refractive index of Y with respect to X will be :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) 10/9
(B) 9/10
(C) 9/8
(D) 8/9
View Answer
Answer: (A)10/9 ✅
📝 Explanation: Refractive index of Y with respect to X
4. Absolute refractive index of water and glass is 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 ×108 m / s the speed of light in water is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) 9/4 ×10⁸ m / s
(B) 7/3×10⁸ m / s
(C) 16/9 × 10⁸ m / s
(D) 9/8 × 10⁸ m / s
View Answer
Answer: (D) 9/8 × 108 m/s ✅
📝 Explanation:
Refractive index (n) = c / v
For glass:
ng = c / vg
c = ng × vg
c = (3/2) × 2 × 108
c = 3 × 108 m/s
For water:
vw = c / nw
vw = (3 × 108) / (4/3)
vw = (9/8) × 108 m/s
- Class 11th Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Class 10th Physics Assertion And Reason PYQ
- Class 10 Physics 3 Marks Questions and Answers | CBSE Board Exam Preparation
- Class 10 Physics 2 Marks PYQ Solutions | CBSE 2025
2. Human Eye
Eye
1. The part of human eye which controls the amount of light entering into it.
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Iris
(B) Cornea
(C) Ciliary muscles
(D) Pupil
View Answer
Answer: (A) Iris ✅
📝 Explanation: The iris controls the size of the pupil and hence regulates the amount of light entering the eye
2. When we focus our eyes on a distance object, the ciliary muscles of our eyes are relaxed. In this case the eye lens becomes
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) thin and its curvature is maximum.
(B) thin and its curvature is minimum.
(C) thick and its curvature is minimum.
(D) thick and its curvature is maximum.
View Answer
Answer: (B) thin and its curvature is minimum ✅
📝 Explanation:
When we look at a distant object, the ciliary muscles relax.
As a result, the eye lens becomes thin.
In this condition, the curvature of the eye lens is minimum, allowing light from distant objects to focus on the retina.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
3. Most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Iris
(B) Pupil
(C) Crystalline lens
(D) Outer surface of Cornea
View Answer
Answer: (D) Outer surface of Cornea ✅
📝 Explanation: The maximum refraction of light entering the eye occurs at the outer surface of the cornea
4. The possible way to restore clear vision of those people whose eyeball has elongated is the use of suitable
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) bifocal lens
(B) concave lens
(C) converging lens
(D) convex lens
View Answer
Answer: (B) concave lens ✅
📝 Explanation: Elongation of the eyeball causes myopia (near-sightedness), which is corrected using a concave lens
5. A boy while reading a book, keeps it much beyond 25 cm from his eyes. This defect of vision has arised because of
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) excessive curvature of the eye lens
(B) the focal length of the eye lens has increased
(C) the eye ball has elongated
(D)the focal length of the eye lens has become too small
View Answer
Answer: (B) the focal length of the eye lens has increased ✅
📝 Explanation: In hypermetropia, the eye lens cannot become sufficiently thick, so its focal length increases, making nearby objects appear blurred
6. The curvature of eye lens of human eye
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) is fixed.
(B) can be increased.
(C) can be decreased.
(D) increases or decreases as the case may be.
View Answer
Answer: (D) increases or decreases as the case may be ✅
Explanation: The ciliary muscles change the curvature of the eye lens to focus objects at different distances
7. An old person is suffering from an eye defect caused by weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens. If the defect of vision is ‘a’ which can be corrected by lens ‘b’, then ‘a’ and ‘b’ respectively are:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) hypermetropia and convex lens
(B) presbyopia and bifocal lens
(C) myopia and concave lens
(D) myopia and bifocal lens
View Answer
Answer: (B) presbyopia and bifocal lens ✅
📝 Explanation: Weakening of ciliary muscles and reduced flexibility of the eye lens causes presbyopia, which is corrected using a bifocal lens
8. The phenomenon responsible for making the smoke particles visible when a beam of sunlight enters a smoke filled room through a narrow hole is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) scattering of light
(B) dispersion of light
(C) reflection of light
(D) internal reflection of light
View Answer
Answer: (A) scattering of light ✅
📝 Explanation: Smoke particles scatter the sunlight, making the path of light visible in the room
9. In the human eye, most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at the surface of:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Cornea
(B)Crystalline lens
(C) Pupil
(D) Aqueous humor
View Answer
Answer: (A) Cornea ✅
📝 Explanation:
Most of the refraction of light entering the human eye occurs at the surface of the cornea
10. The part of the human eye which can modify the curvature of the eye lens to some extent is :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Pupil
(B) Cornea
(C) Ciliary muscles
(D) Aqueous humour
View Answer
Answer: (C) Ciliary muscles ✅
📝 Explanation:
Ciliary muscles change the curvature of the eye lens to focus light from objects at different distances
Prism
1. The white light entering a glass prism, gets split into its constituent colors. It is observed that:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Red light deviates the most.
(B) Violet light deviates the least.
(C) Yellow light deviates more than the blue light.
(D) Green light deviates more than the orange light.
View Answer
Answer: (D) Green light deviates more than the orange light ✅
Explanation: In a prism, shorter wavelength light deviates more; hence green light deviates more than orange light
2. In the given figure the angle of incidence and the angle of deviation respectively are:
[CBSE 2024-25]
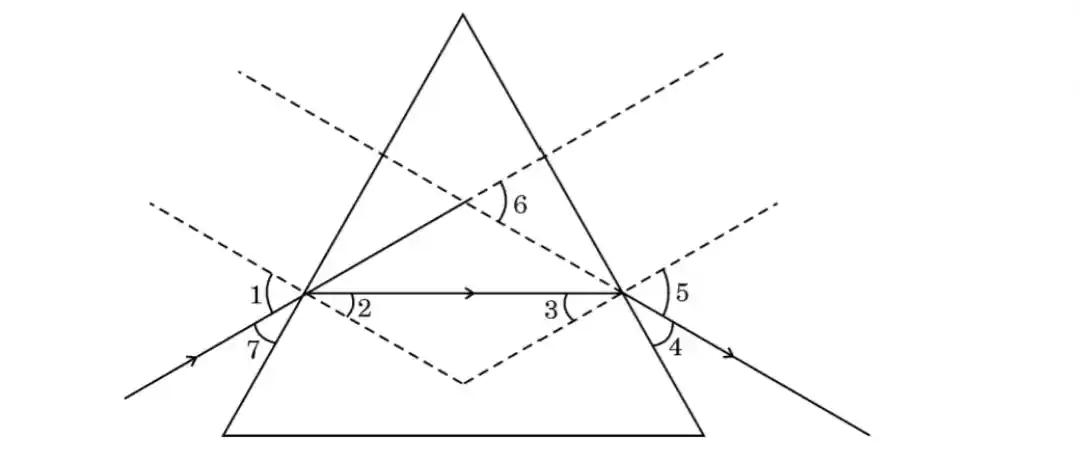
(A) 1 and 5
(B) 7 and 6
(C) 7 and 4
(D) 1 and 6
View Answer
Answer: (D) 1 and 6 ✅
📝 Explanation:
Angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray → 6
Angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal at the first surface → 1
Scattering Of Light
1. When a beam of white light passes through a region of very fine dust particles, the colour of light that scatters the most in that region is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) red
(B) orange
(C) blue
(D) yellow
View Answer
Answer: (C) Blue ✅
📝Explanation:
Very fine dust particles scatter light of shorter wavelength more effectively.
Blue light has the shortest wavelength among the given options.
Therefore, blue light is scattered the most in a region containing very fine dust particles.
2. When a beam of white light passes through a region of very fine dust particles, the colour of light that scatters the most in that region is :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) red
(B) orange
(C) blue
(D) yellow
View Answer
Answer: (C) blue ✅
📝 Explanation:
Very fine dust particles cause scattering of light.
Light of shorter wavelength scatters more than light of longer wavelength.
Among the given options, blue light has the shortest wavelength.
Hence, blue light is scattered the most.
3. Select the correct statement from the following :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) The size of the molecules of air is larger than the wavelength of visible light.
(B) The blue light has a wavelength about 1.8 times greater than that of red light.
(C) When sunlight passes through the fine particles in air, they scatter the blue colour of visible light more strongly than red.
(D) The light of red colour is scattered the most by fog or smoke.
View Answer
Answer: (C) ✅
📝 Explanation:
The scattering of light by very fine particles in air depends on the wavelength of light.
According to Rayleigh scattering, light of shorter wavelength is scattered more strongly than light of longer wavelength.
Blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light.
Therefore, when sunlight passes through fine particles in air, blue light is scattered more than red light.
3. Electricity
Ohm’s Law
1. The resistivity of a wire made of an alloy is generally:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) Lower than that of its constituent metals.
(B) Higher than that of its constituent metals.
(C) Decreases with increase in its area of cross-section.
(D) Increases with increase in its length.
View Answer
Answer: (B) Higher than that of its constituent metals ✅
Explanation:
Alloys have higher resistivity than pure metals because the presence of different atoms increases scattering of electrons, opposing current flow
2. A wire of length ‘L’ is gradually stretched so that its length increases to 3L. If its original resistance is R, then its new resistance will be :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) 3R
(B) 6R
(C) 9R
(D) 27R
View Answer
Answer: (C) 9R ✅
📝 Explanation:
When a wire is stretched, its volume remains constant.
Let original length = L and original resistance = R
New length = 3L
Since volume is constant:
A × L = A’ × 3L
So, new area A’ = A / 3
Resistance R = ρL / A
New resistance R’ = ρ(3L) / (A/3)
R’ = 9 × (ρL / A)
R’ = 9R
Therefore, the new resistance of the wire is 9R.
Combination of Resistors
1. Four identical resistors of 12 ohm each are connected in series to form a square ABCD as shown in the figure. The resistance of the network between the two points 1 and 2 is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
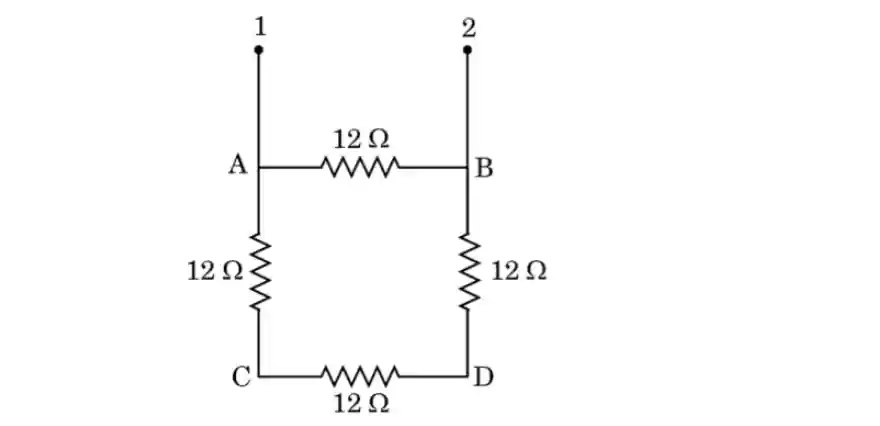
(A) 48 Ω
(B) 36 Ω
(C) 9Ω
(D)6Ω
View Answer
Answer: (C) 9 Ω ✅
📝 Explanation:
Four identical resistors of resistance 12 Ω each are connected to form a square ABCD.
The resistance is to be calculated between points 1 and 2, which are connected to points A and B respectively.
Between points A and B, there are two possible paths for current flow:
Path 1 (Direct path A → B):
This path contains only one resistor of 12 Ω.
Path 2 (Long path A → C → D → B):
This path contains three resistors in series:
12 Ω + 12 Ω + 12 Ω = 36 Ω
Thus, the two paths between A and B have resistances 12 Ω and 36 Ω respectively.
Since both paths connect the same two points (A and B), they are in parallel combination.
Using the formula for equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel:
R = (R1 × R2) / (R1 + R2)
R = (12 × 36) / (12 + 36)
R = 432 / 48
R = 9 Ω
Therefore, the resistance of the network between points 1 and 2 is 9 Ω.
2. A piece of wire of resistance ‘R’ is cut lengthwise into three identical parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R’, then the value of R/R’ is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(a) 1/9
(b) 1/3
(c) 3
(d) 9
View Answer
Answer: (d) 9 ✅
📝 Explanation:
Let the original resistance of the wire be R.
When the wire is cut into three equal lengths, the length of each part becomes l/3.
Since resistance is directly proportional to length:
Resistance of each part = R / 3
The three equal resistors (each of resistance R/3) are connected in parallel.
Equivalent resistance R′ of three equal resistors in parallel is:
R′ = (R/3) / 3
R′ = R / 9
Therefore,
R / R′ = R / (R/9) = 9
3. In case of wires of same resistivity, the resistance of the wire will be maximum if the diameter and length of the wire respectively are
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) D and L
(B) D/2 and L/4
(C) D/3 and L/6
(D) D/4 and L/12
View Answer
Answer: (C) D/3 and L/6 ✅
📝 Explanation:
Resistance of a wire is given by:
R = ρL / A
For wires of the same material, resistivity (ρ) is constant.
Area of cross-section A ∝ D2
So,
R ∝ L / D2
Now compare each option:
(A) R ∝ L / D2
(B) R ∝ (L/4) / (D/2)2 = L / D2
(C) R ∝ (L/6) / (D/3)2 = (9/6) × L / D2
(D) R ∝ (L/12) / (D/4)2 = (16/12) × L / D2
Option (C) gives the maximum value of resistance.
Hence, the resistance will be maximum when the diameter is D/3 and the length is L/6.
Electric Power, Heat and Energy
4. The resistance of a wire is 40 2. If 2 A of current flows through this wire for 50 seconds, the heat produced in the wire is
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) 4000 J
(C) 16000 J
(B) 8000 J
(D) 80000 J
View Answer
Answer: (B) 8000 J ✅
Explanation:
Given:
Resistance (R) = 40 Ω
Current (I) = 2 A
Time (t) = 50 s
Heat produced in a conductor is given by Joule’s law:
H = I2 R t
Substituting the given values:
H = (2)2 × 40 × 50
H = 4 × 40 × 50
H = 8000 J
Therefore, the heat produced in the wire is 8000 joules.
5. An electric bulb is rated 220 V; 11W. The resistance of its filament when it glows with a power supply of 220 V is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(a) 4400 Ω
(b) 440 Ω
(c) 400 Ω
(d) 20 Ω
View Answer
Answer: (a) 4400 Ω ✅
📝 Explanation:
Given:
Voltage (V) = 220 V
Power (P) = 11 W
Using the relation:
P = V2 / R
So,
R = V2 / P
R = (220 × 220) / 11
R = 48400 / 11
R = 4400 Ω
Hence, the resistance of the filament is 4400 Ω.
6. The minimum number of identical bulbs of rating 4V; 6W, that can work safely with desired brightness, when connected in series with a 240 V mains supply is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(a) 20
(b) 40
(c) 60
(d) 80
View Answer
Answer: (c) 60 ✅
📝 Explanation:
Each bulb is rated at 4 V, which means it can safely operate at a maximum voltage of 4 V.
Total supply voltage = 240 V
When bulbs are connected in series, the supply voltage is divided equally among them.
Number of bulbs required = Total voltage / Voltage rating of one bulb
Number of bulbs required= 240 / 4
Number of bulbs required= 60
Therefore, a minimum of 60 identical bulbs must be connected in series to work safely with desired brightness.
7. An electric bulb is connected to a power supply of 220 V. If the current drawn by the bulb from the supply is 500 mA, the power of the bulb is:
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) 11 W
(B) 110 W
(C) 220 W
(D) 1100 W
View Answer
Answer: (B) 110 W ✅
📝 Explanation:
Power (P) = V × I
P = 220 × 0.5
P = 110 W
4. Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current
Magnet
1. Which one of the following statements is not true about a bar magnet?
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) It sets itself in north-south direction when suspended freely.
(B) It has attractive power for iron filings.
(C) It produces magnetic field lines.
(D) The direction of magnetic field lines inside a bar magnet is from its north pole to its south pole.
View Answer
Answer: (D) ✅
📝 Explanation:
A bar magnet, when suspended freely, always aligns itself in the north–south direction.
It has the ability to attract iron filings and produces magnetic field lines around it.
Outside the bar magnet, magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole.
However, inside the bar magnet, the magnetic field lines run from the south pole to the north pole.
Therefore, statement (D) is not true.
Solenoid
1. The strength of magnetic field produced inside a long straight current carrying solenoid does not depend upon :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) number of turns in the solenoid
(B) direction of current flowing through the solenoid
(C) material of the core filled inside the solenoid
(D) radius of the coil of the solenoid
View Answer
Answer: (B) direction of current flowing through the solenoid ✅
📝 Explanation:
The strength of magnetic field inside a long straight current-carrying solenoid depends on:
* Number of turns per unit length of the solenoid
* Magnitude of current flowing through it
* Nature of the core material inside the solenoid
Changing the direction of current only reverses the direction of the magnetic field, but does not change its strength.
Therefore, the magnetic field strength does not depend on the direction of current.
Force on Current Carrying Conductor
1. A steady current flows through a thick horizontal straight wire from east to west. The direction of the magnetic field produced at a point above the wire is towards
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) North
(B) South
(C) East
(D) West
View Answer
Answer: (A) North ✅
📝 Explanation:
Explanation (Using Right-Hand Thumb Rule):
- Current flows from east to west.
- Point of observation is above the wire.
- According to the Right-Hand Thumb Rule:
- Point the thumb of your right hand in the direction of current (east → west).
- The curl of fingers gives the direction of the magnetic field.
👉 At a point above the wire, the curled fingers point towards the North.
✔ Magnetic field is directed towards North
2. A uniform magnetic field
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) always exerts a force on a current carrying conductor.
(B) never exerts a force on a current carrying conductor.
(C) exerts a force only when current flows through a conductor along the direction of the field.
(D) exert a force only when current flows through a conductor at right angles to the field.
View Answer
Correct Answer: (D) ✅
📝 Explanation:
A current-carrying conductor experiences a force in a magnetic field only when the direction of current is not parallel to the magnetic field.
The force is maximum when the conductor is placed at right angles to the magnetic field.
If the conductor is placed along the direction of the magnetic field, no force acts on it.
Therefore, a uniform magnetic field exerts a force only when current flows through a conductor at right angles to the field.
3. In domestic electric circuits, the color of insulation covers of wires in the cables of electric iron/electric toaster is generally :
[CBSE 2024-25]
(A) red for live wire, green for neutral wire and black for earth wire
(B) red for live wire, black for neutral wire and green for earth wire
(C) green for live wire, black for neutral wire and red for earth wire
(D) green for live wire, red for neutral wire and black for earth wire
View Answer
Answer: (B) ✅
📝 Explanation:
In domestic electric circuits, standard colour codes are used for safety.
Red wire is used for the live (phase) connection.
Black wire is used for the neutral connection.
Green wire is used for the earth connection.
Hence, the correct colour combination is red for live, black for neutral and green for earth.
❓FAQs
Yes, these MCQs are useful for school exams, unit tests, pre-boards, and board exams.
Yes, each MCQ is provided with the correct answer and a short, exam-oriented explanation for easy understanding.
Yes, all questions are based on the latest CBSE Class 10 Physics syllabus.
Yes, many MCQs are repeated or conceptually similar in board exams.
With regular PYQ practice and concept clarity, scoring high is possible.