Magnet
Magnet is an object which attracts pieces of iron, nickel and cobalt. towards itself.
Magnet are different shape:
- Bar Magnet
- Horse shoe shaped magnet
- Magnetic needle
- Magnetic compass
Some Facts About Magnets
1. Magnet always exist as dipole.
2. When magnet is freely suspended it always aligns towards north-south direction.
3. Like pole always repel and opposite poles attract each other.
4. Two poles can never be separated.
Oersted’s Experiment
Hans Christian Oersted discovered that electric current produces a magnetic effect.
In his experiment, he took a straight wire connected to a battery and placed a compass needle near the wire.
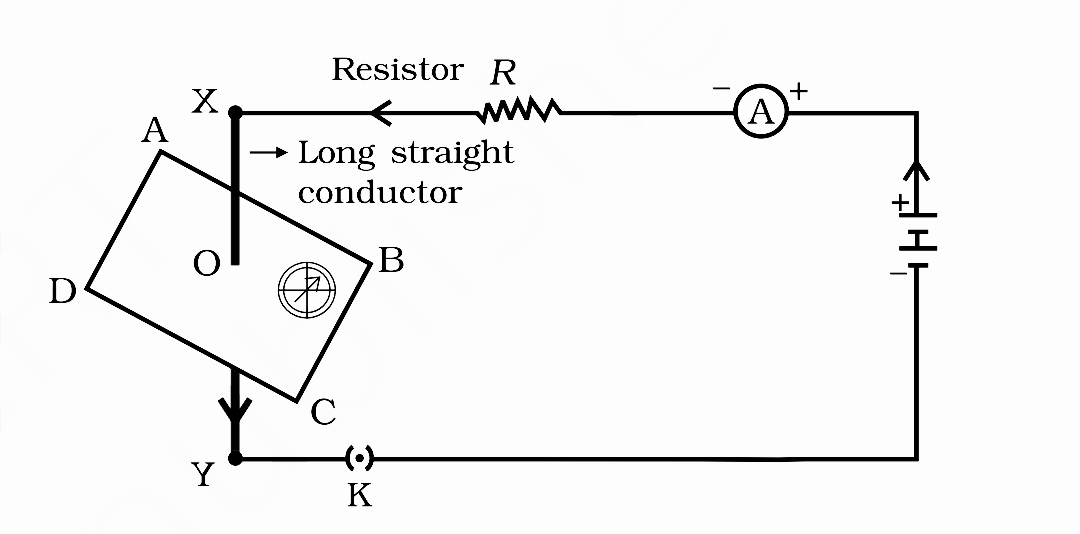
When the electric current was switched ON, the compass needle deflected from its normal north–south direction.
When the current was switched OFF, the needle returned to its original position.
This showed that a magnetic field is produced around a current-carrying conductor, and this magnetic field causes the compass needle to move.
Magnetic Field Lines
Imaginary lines which represents magnetic field around a magnet, are called magnetic field lines.
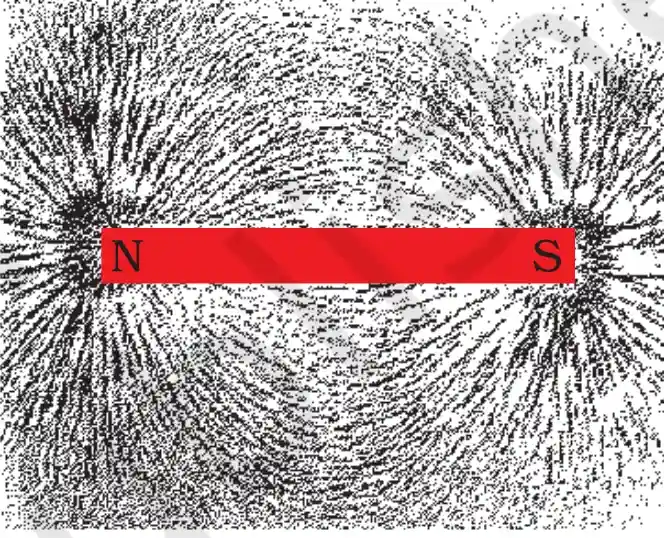
Properties of Magnetic Field Lines
- Magnetic field lines always originate from north pole and terminate at South pole.
- Magnetic Field lines are always closed curve.
- Two magnetic field lines never cross each other.
- Magnetic field lines is strong if they are closer and vice-versa.
- Tangent to magnetic field lines shows direction of field.
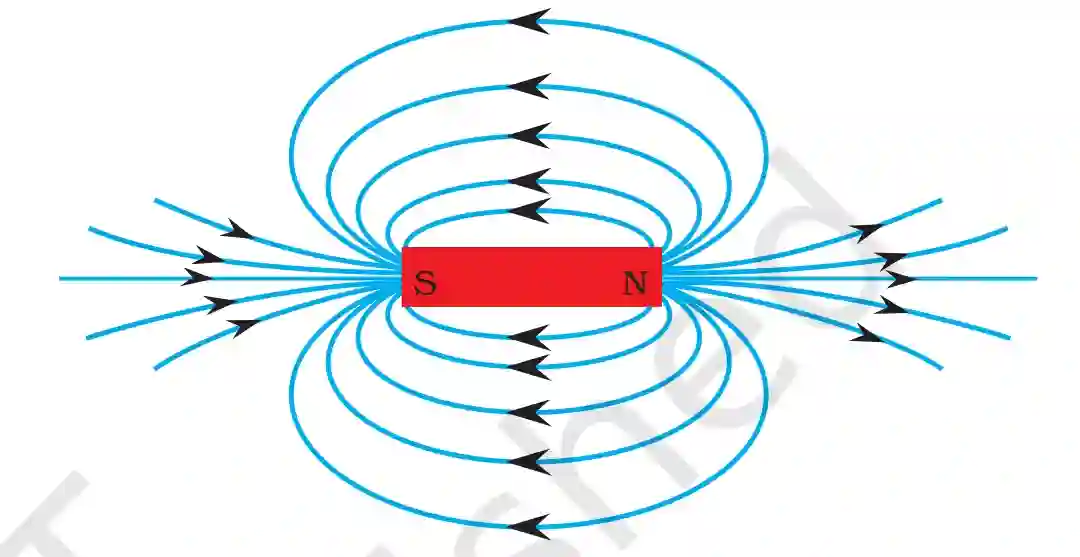
Note: Magnetic field is studied by drawing imaginary lines called magnetic lines of forces.
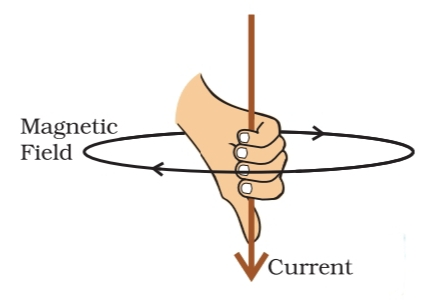
Right Hand Thumb Rule
If we hold a wire with our right hand and keep our thumb in the direction of the current flowing in the wire, then the bent fingers show the direction of the magnetic field generated due to the current.
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight
Conductor
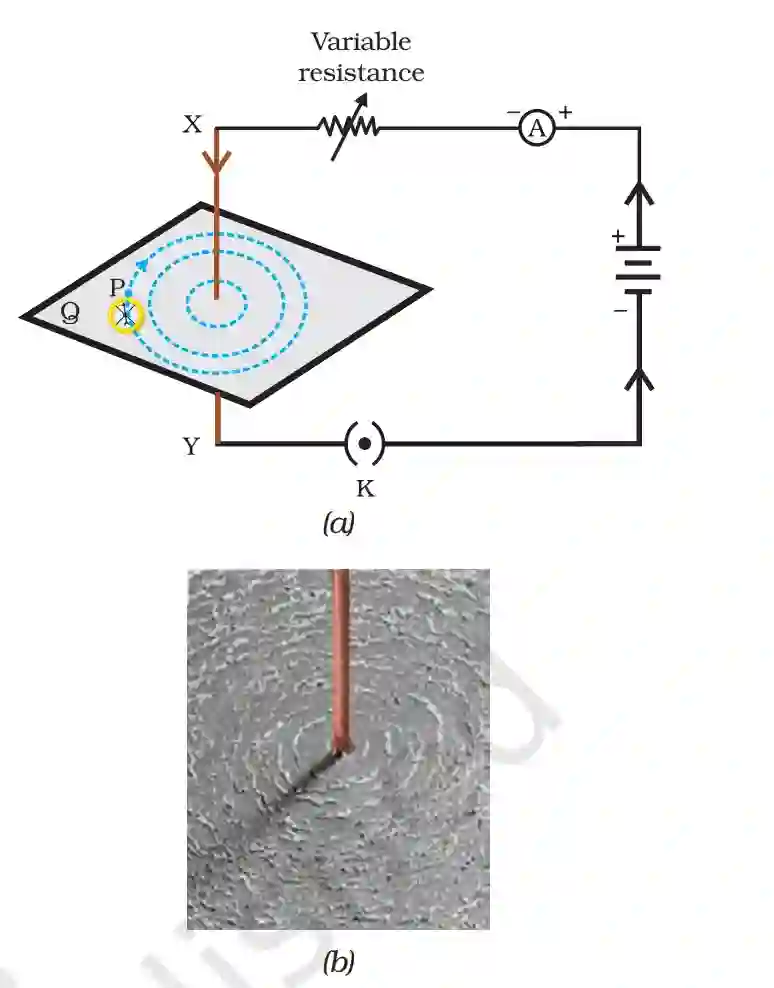
Shape of magnetic field for straight wire is in the form of concentric circles having centre as its conductor.
Factor affecting magnetic field for straight conductor:
1. Current: Magnetic field strength is directly proportional to the amount of current flowing in conductor.
2. Distance: Magnetic field strength is inversely proportional to the distance from conductor.
3. Direction of current: If direction of current changes, if changes the direction of magnetic field.
Right-Hand Thumb Rule
If you hold a wire carrying current in your right hand and point your thumb in the direction of the current, then the way your fingers curl shows the direction of the magnetic field around the wire.
Magnetic Field due to Current Carrying Circular Loop:
When a straight current-carrying wire is bent into a circular loop, it produces a magnetic field around it.
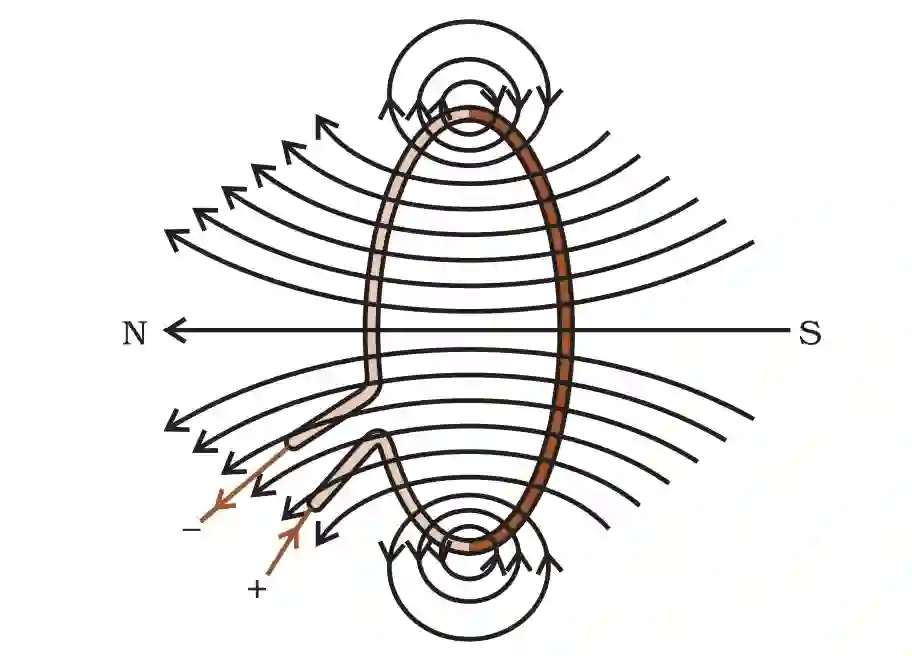
The magnetic field lines form concentric circles near the wire, and these circles become larger as we move away from the loop.
At the center of the loop, these large circles appear as straight, parallel lines.
Every part of the loop creates a magnetic field, and all these fields add up in the same direction at the center.
The direction of the magnetic field can be found using the Right-Hand Thumb Rule
Factor affecting magnetic field for circular loop:
1. Current in the loop: Magnetic field is directly proportional to the current in the loop.
2. Radius of loop: Magnetic field is inversely proportional to the radius of loop for same current.
3. Distance from loop: Magnetic field is inversely proportional to the distance from loop.
Solenoid
A solenoid is a long coil of wire wound closely in the shape of a cylinder.When electric current passes through it, the solenoid behaves like a bar magnet with a north pole and south pole.
Key Point
- A solenoid produces a uniform magnetic field inside it, just like a bar magnet.
- The end where the current flows anticlockwise behaves like the north pole.
- The end where the current flows clockwise behaves like the south pole.
- The magnetic field inside a solenoid is strong, straight, and parallel.
- A soft iron core placed inside a solenoid becomes a strong electromagnet.
- The strength of the magnetic field increases when:
- Current increases
- Number of turns increases
- Soft iron core is used
Magnetic Field Produced due to Solenoid
Factors affecting magnetic field of solenoid
1. Current in Solenoid: magnetic field is directly proportional to the current flowing in solenoid.
2. Number of turns in solenoid: Magnetic field is directly proportional to the number of turns per unit length.
3. Distance from solenoid: Magnetic field is inversely proportional to the distance from the solenoid.
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet that works only when electric current flows through it.
Difference between Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet
| 1. A magnet that always shows magnetism. | A magnet that works only when electric current flows. |
| 2. Cannot be switched ON or OFF | Can be switched ON or OFF. |
| 3. Fixed strength, cannot be changed easily. | Strength can be increased by increasing current or coil turns |
| 4. Made from hard magnetic materials like steel. | Made by winding a coil around a soft iron core |
| 5. Generally weaker compared to electromagnets. | Can be made very strong. |
| 6. Compasses, fridge magnets, speakers. | Cranes, motors, relays, electric bells. |
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
If we stretch our fore finger, middle finger and thumb mutually perpendicular to each other such that fore finger points in the direction of magnetic field middle finger indicates direction of current then thumb give the direction of force or motion of the conductor.
Force on a current-carrying conductor in magnetic field:
French scientist Andre Marie Ampere suggest that whenever current carrying conductor is placed inside an external magnetic field, it experiences a force which is perpendicular to the both magnetic field and current.
Reason of Force: Conductor produces its own magnetic field and this magnetic field interact with external magnetic field and hence conductor experiences force.
Domestic Electric Circuit
Earthing
Electric appliances are always touched by hands, there can be a chance that its insulation breaks or cracks, them its bare wires touches its metal cases than the person touching them might get a shock. To avoid such the metal cases are earthed.
By earthing we mean that the metallic body is connected to thick copper wire which is buried deep under earth. And at the end of copper plate is surrounded by mixture of charcoal and common salt.
The earth is always at 0 potential. So, if an electric appliance gets short circuit metal body to the earth like if magnitude of current rises due to short circuit the fuse wire melts but the appliance will not receive any current as it is earthen.
Important Definition
Overloading
Overloading of an electric circuit means when current flows in a circuit it becomes more than the capacity of components in the circuit to resist the current. When too much current passes in an electric circuit, overload occurs through electric wires, which may cause fire to break.
Note: Fuse and MCB are used to avoid overloading.
Short-Circuiting
A short circuit is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with very low electrical resistance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit, which may cause fire to break.
Note: We should keep checking the insulation to avoid short circuit.
Question: What is advantageous to use domestic circuit in parallel than series.
Answer:
Independent Operation: Appliances work independently; one failure doesn’t affect others.
Equal Voltage: All appliances receive the same voltage as the supply.
Varied Current: Different appliances can draw the required current.
Energy Efficient: Appliances can be used individually, saving energy.Safety: Reduces overheating risks.
Difference between AC and DC
| Alternates direction periodically. | DC: Flows in one constant direction. |
| Generated by power plants (e.g., mains electricity). | Provided by batteries, solar cells. |
| Can be easily transformed to different voltages. | Difficult to change voltage. |
| Used for homes and industries. | Used in electronic devices and vehicles. |
| Efficient for long-distance transmission. | Less efficient over long distances. |
Kicking Wire Experiment
On pressing the switch current flows in wire in downward direction as it is placed between poles of magnet because force acts on it and wire gets displaced from its original position.
As it gets displaced, circuit breaks, current flows stops due to which no force acts on wire and it returns to its original position.
Again circuit gets completed, again force acts and wire get displaced.
This is how it goes on repeating.