Keywords
Temperature: The degree of hotness or coldness of an object is called temperature.
Thermometer: A device or instrument that is used to measure temperature is called thermometer.
Conduction: The method in which heat is transferred by the vibration of molecules is called conduction.
Convection: The method in which heat is transferred by the movement of molecules is called convection.
Radiation: The method in which transfer of heat does not need any medium to travel is called radiation.
Heat: Heat is a form of energy that causes the sensation of warmth or coldness in us.
Temperature: The degree of hotness or coldness of an object is called temperature.
Difference between Heat and Temperature
| Heat | Temperature |
|---|---|
| 1. Heat is a form of energy. | 1. Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness. |
| 2. Heat causes a change in the temperature of the body. | 2. Temperature is the effect of heat. |
| 3. Heat is measured in calories or joules. | 3. Temperature is measured in degree Celsius or degree Fahrenheit. |
Temperature Scales
There are three scales on which the temperature is measured and expressed. These are Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
Celsius Scale
Anders Celsius, a Swedish physicist, introduced the Celsius scale in 1742. It divides the range between the freezing and boiling points of water into 100 equal parts. 0°C is the freezing point, and 100°C is the boiling point. Temperatures on this scale are denoted with °C (degrees Celsius).
Fahrenheit Scale
The Fahrenheit scale, created by German physicist D. G. Fahrenheit in 1724, divides the range between the freezing and boiling points of water into 180 equal parts. 32°F represents the freezing point, and 212°F represents the boiling point. Temperatures on this scale are noted with °F (degrees Fahrenheit).
Kelvin Scale
The Kelvin scale, developed by Lord Kelvin in 1848, divides the range between its fixed points into 100 equal parts. The lower point is 273 K (absolute zero) and the upper point is 373 K (boiling point of water).
Kelvin is the SI unit for temperature.
Temperature in different scales
| Object | On Celcius Scale | On Fahrenheit Scale | On Kelvin Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting point of ice(Lower fixed point) | 0 ºC | 32 ºF | 273K |
| Boiling point of water( Upper fixed point) | 100 ºC | 212 ºF | 373K |
| Normal human body | 37 ºC | 98.6ºF | 309K |
Relationship Between Different Scales of Temperature
Though the temperature shown by the different scales is different, yet they can be converted and expressed in terms of each other. If the temperature of an object is measured in °C, it can be converted into °F and vice-versa. For converting temperature expressed on a different scale, following equations can be used:
\frac{C}{5}=\frac{F−32}{9}
K=C+273
Thermometers
A thermometer measures temperature. Common types include liquid-in-glass, digital, and infrared. In a liquid-in-glass thermometer, mercury expands or contracts with temperature changes. Digital thermometers show readings digitally and are quicker. Infrared thermometers measure temperature without touching the object. Thermometers are crucial in various fields like medicine, weather forecasting, and cooking for accurate temperature monitoring.
The most commonly used thermometers are laboratory thermometer,clinical thermometer and digital thermometer.
Clinical Thermometer
A clinical thermometer is designed to measure human body temperature. It typically has a narrow range, such as 35-42°C, with markings in Celsius or Fahrenheit. These thermometers are used orally, rectally, or underarm.
Precaution while using a thermometer
- Clean with antiseptic before and after each use.
- Hold close to your eyes, tilted.
- Hold from the stem, not the bulb.
- Mercury below 35°C; jerk if not.
- Don’t hit on hard objects; mercury is toxic if broken.
Digital Thermometer
Mercury is a toxic substance and is very difficult to dispose of if a thermometer breaks. These days, digital thermometers are used which do not require mercury. A digital thermometer is a good replacement of a mercury clinical thermometer. In a digital thermometer, the temperature is displayed in a numeric form.
Effect Of Heat
When an object is heated, some changes occur in it. Some of them are as follows.
- Change in Temperature
- Change in the state of matter
- Change in appearance
- Change in volume
Transfer Of Heat
There are three methods of heat transfer.
Conduction
Conduction is the method in which heat is transferred by vibration of molecules and there are no actual movement of molecules in the object which is heated.
Convection
Convection is the method in which heat is transferred by movement of molecules.
Radiation
The method of transfer of heat that does not need any medium to flow is called radiation and it is the fastest method of transfer of heat.
Note: Our body radiates heat to the surroundings and receives heat from the surroundings by radiation.
Difference between the three methods of transfer of heat
| S.No. | Basis of difference | Conduction | Convection | Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Presence of medium | Needed | Needed | Not needed |
| 2. | Behaviour of molecules of medium | Molecules vibrate | Molecules move | Molecules do not move or vibrate |
| 3. | Speed | Slow process | Slow process | Very fast process |
| 4. | Path of travel of heat | In any direction | In any direction | In straight line |
| 5. | Used for heating | Solids | Liquid and gases | All state of matter |
| 6. | Can take place in vacuum | No | No | Yes |
| 7. | Role played by colour of objects | No | No | Dark coloured objects absorb more heat |
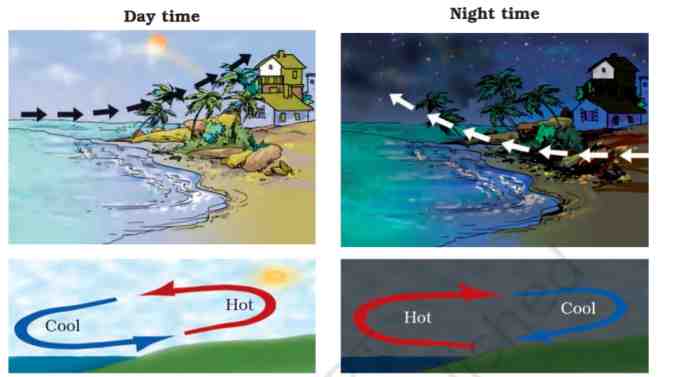
Sea Breeze
During the day, when the Sun shines, the land and sea get heated but the land gets heated faster than the water in the sea. The air over the land becomes warmer and rises. As a result, cool air from the sea blows in to take its place, called sea breeze.
Land Breeze
During the night when there is no Sun, the land and sea start getting cool. But, the land gets cooler faster than the water in sea so, the air over the sea becomes warmer and rises up. As a result, cool air from land blows out to take its place, called land breeze.
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat NCERT Exercise Solution
NCERT Exercise
1. State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
2. Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
3. Fill in the blanks :
(a) The hotness of an object is determined by its __________.
(b) Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a________ thermometer.
(c) Temperature is measured in degree _________.
(d) No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of__________.
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. Heat is transferred to its other end by the process of ______________.
(f ) Clothes of ______________ colours absorb more heat better than clothes of light colours.
4. Match the following :
| (i) Land breeze blows during | (a) summer |
| (ii) Sea breeze blows | (b) winter |
| (iii) Dark-coloured clothes are preferred during | (c) day |
| (iv) Light-coloured clothes are preferred during | (d) night |
5. Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing.
6. Look at Fig. 3.13. Mark where the heat is being transferred by
conduction, by convection and by radiation.
7. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
8.One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be
(a) 80°C
(b) more than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C
(d) between 30°C and 50°C
9.An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C.
The heat will
(a) flow from iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
10.A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end
(a) becomes cold by the process of conduction.
(b) becomes cold by the process of convection.
(c) becomes cold by the process of radiation.
(d) does not become cold.
11. Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that
(a) copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
(b) such pans appear colourful.
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel.
(d) copper is easier to clean than the stainless steel.
Additional Exercise
A. Tick (✓) the correct options.
1. Which of these is not a scale for measuring temperature?
a) Kelvin
b) Galileo ✓
c) Celsius
2. At what reading is the temperature on Celsius and Fahrenheit scale same?
a) 40
b) 0
c) -40 ✓
3. Who invented thermometer?
a) D. G. Fahrenheit ✓
b) Anders Celsius
c) Lord William
4. Which of these does not use mercury?
a) Clinical thermometer
b) Laboratory thermometer
c) Digital thermometer ✓
5. How is heat transferred in liquids and gases?
a) Conduction
b) Convection ✓
c) Radiation
B. Fill in the blanks.
1. ………….is the degree of hotness or coldness of an object.
2. Water boils at …………..°C.
3. A …………… is present in clinical thermometer to prevent fall in mercury level.
4. We should always hold the thermometer from ……….. and not from …………
5. Heat is transferred in ……… by conduction.
Answer – 1. Temperature, 2. 100, 3. kink 4. stem, the bulb 5. solid
C. Match the columns.
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1.Conduction | a.S I. unit of temperature |
| 2.Convection | b.Conductor of heat |
| 3.Celsius scale | c.No medium needed |
| 4.Mercury | d.Vibration of molecules |
| 5.Radiation | e.Most commonly used scale |
| 6.Kelvin | f.Movement of molecules |
Answer- 1-d, 2-f, 3-e, 4-b, 5-c, 6-a
D. State whether the following statements are “True or False
1. Kelvin scale was given by Lord William.
2. Melting point of ice is 32°C.
3. The Celsius and Kelvin scales show same readings.
4. We should wear light-coloured clothes in winter.
5. Laboratory thermometer should be held in tilted position close to eyes.
answer – 1. True, 2. False, 3. False, 4. False, 5.False
Very helpfull for me, thanks
Thanks
Thanks
Thank you so much
This website is a very wonderful for study
Full Support for this Website🙏🥰
Thanks
Full welcome 🤗